
Titanium Coated PEEK
Enhanced Bone Contact
Medacta's TiPEEK cages represent the next generation plasma sprayed Ti-Coated interbody fusion device designed for optimal clinical evaluation. TiPEEK promotes bony ongrowth, maintains the radiolucency accustomed to with PEEK polymer and provides improved stability. The TiPEEK lumbar posterior and anterior cages, as well as cervical devices, are available in numerous footprints, heights, and sagittal profiles to accommodate various patients.

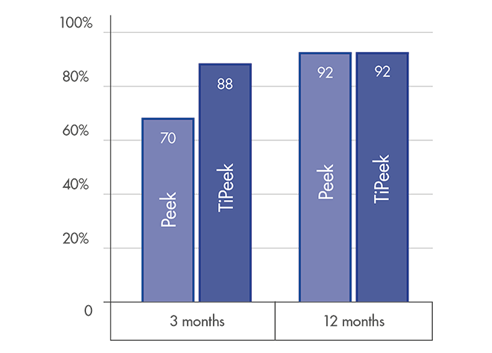
FUSION RATE
High level fusion rate: ~90% at 3 months post-operatively [1]
Optimal solution for accelerated fusion[1] & fast bone remodelling[2]
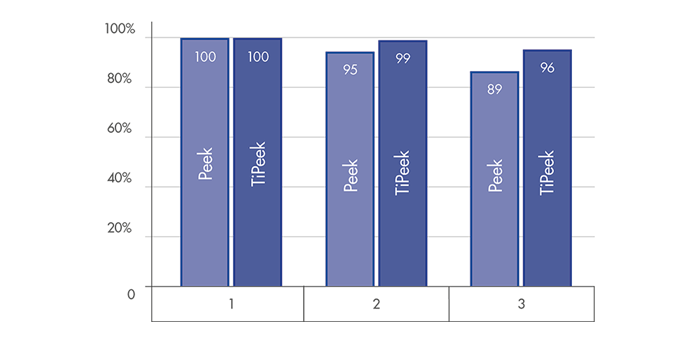
DISC HEIGHT PRESERVATION
Superior behavior for a substantial interbody height restoration and lordosis maintenance[1]
Highly reduced subsidence risk for optimal interverterbral height preservation [1]
*according to the FDA guidance, ISO and ASTM standard for tensile, shear, abrasion and compression strength for metallic spray coatings.
TiPEEK bioactive cages may promote bone fusion [1] and facilitate bone formation [2]

The unique TiPEEK cages may participate in bony fusion processes and increase bone quality [2]
TiPEEK stimulates bone apposition:

Superficial bone ongrowth around the Ti-Coating texture [2]

Bone ingrowth with fusion mass formation through the cage interior side [3]
In vivo bone growth increases with time demostrating maturation and remodelling of the newly formed bone [2]
Rough, micro-textured TiPEEK surface may lead to several implications:
an improved primary stability due to an increased surface friction
enhanced secondary stability thanks to rapid bone apposition, mineralisation and maturation [2]
increased migration resistance for short and long term stability [2]
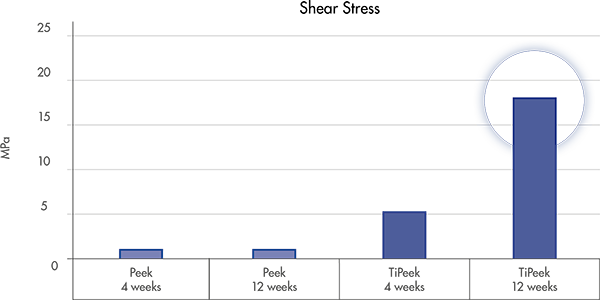
Test performed on Ovine (16)
TiPEEK cages are compatible with the diagnostic bio-imaging techniques and provide a clear fusion assessment
Unlike solid full Titanium cages or porous Tantalum which create significant artefacts [5,6], radiolucent TiPeek technology allows for:

Appropriate spine support
PEEK core provide a native bone interface[7,8] that may help preventing the subsidence[10]
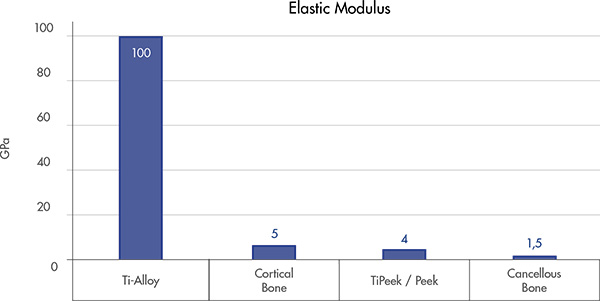
Physiological load Sharing
Helps to reduce the stress shielding and to facilitate bony fusion[9]
Allows for proper load force transmission at the implant-tissue interface[9]
Support bone formation and reduce osteolysis[9]

Improved biocompatibility actively participating in the fusion process [12]
Osteoconductive surface to promote osseointegration with the surrounded bone [12]

ROUGH LAYER
Complex micron scale roughness promote osteoblastic differentiation and increase bone formation[13,14]
HYDROPHILIC SURFACE
Micro structured Titanium Spray creates hydrophilic surfaces which may improve neovascularization and subsequently implant osseointegration[14]
LOW INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE
Ti-coated surfaces reduce inflammatory response with reduced risk of fibrous tissue layer around the implant while driving direct bone formation[12]

MYSPINE
Patient Matched Technology
MySpine is a tailor made patient specific guide for spine procedures based on the established MyKnee technology.
The guide is intended to lead the surgeon during the critical steps of accurate pedicle screw placement whilst reducing the surgical time and intra-operative X-ray radiation.

M.U.S.T.
Screw System
The M.U.S.T. Pedicle Screw System is an unconstrained polyaxial screw, rod & connector design applicable to degenerative, deformity and trauma indications using traditional open or MIS surgical approaches

M.U.S.T. MIS Platform
The MUST MIS Platform represents an effective and harmonic concept in terms of minimally invasive solutions. The Mini Open retractor along with the MUST Percutaneous system, can drive the surgeon through an efficient spine surgery result.
[2] B.Walsh et al. Titanium coated interbody devices
[4] M. Rauschmann et al, Osteoporotic patients in spine surgery
[5] Withmore et al. J Spine Neurosurg 2013, 2:4
[6] Wang JC Spine 1 August 1998 - Volume 23 - Issue 15 - p 1684–1688
[7] Kuhn JL, et al.. Comparison of the trabecular and cortical tissue moduli from human iliac crests. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(6):876-84.
[8] Babyn JD et al. Characterization of a new porous tantalum biomaterial for reconstructive orthopaedics. Proceedings of AAOS, Anaheim, CA. 1999
[9] Sagomonyants KB, Biomaterials 29 (2008) 1563-1572
[10] Chen et al. Comparison of titanium and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages in the surgical treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a prospective, randomized, control study with over 7-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2013 Jul;22(7):1539-46.
[12] Buser D et al. J Biomed Mater Res 1991;25(7):889-902
[13] Olivares-Navarrete et al. Implant materials generate different peri-implant inflammatory factors: poly-ether-ether-ketone promotes fibrosis and microtextured titanium promotes osteogenic factors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015 Mar 15;40(6):399-404
[14] Olivares-Navarrete et al. Osteoblast maturation and new bone formation in response to titanium implant surface features are reduced with age. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(8); 1773-1783
[15] Pelletier et al. Interbody fusion with peek and a novel compliant titanium fusion device in an aged ovine model. Proceedings of ORS Annual Meeting, 2010, (poster n.1397)
[16] M.O.R.E. Journal 2017, Effect of titanium coating on PEEK osteoconductivity in an ovine model